The Advanced Query Builder is being introduced as an enhancement to improve filtering capabilities within the Logs Page. The existing traditional query builder lacks support for logical operators like AND and OR, limiting users to basic attribute-value filtering.
Users can switch to Advanced Query Mode for more complex filtering.
Supports multiple operators to refine log searches effectively.
Affects the Logs Explorer Page, Log Alerts, Metric Definitions, Live Tail, and Log Tiles in Dashboards.
Label search helps users filter logs by specific label values using different operators. Users define a label, choose an operator, and assign a value to create queries that refine log searches.
When users hover over the field, the system displays all available operation query functions, and users choose the required one. They can still enter the query functions manually if they prefer.
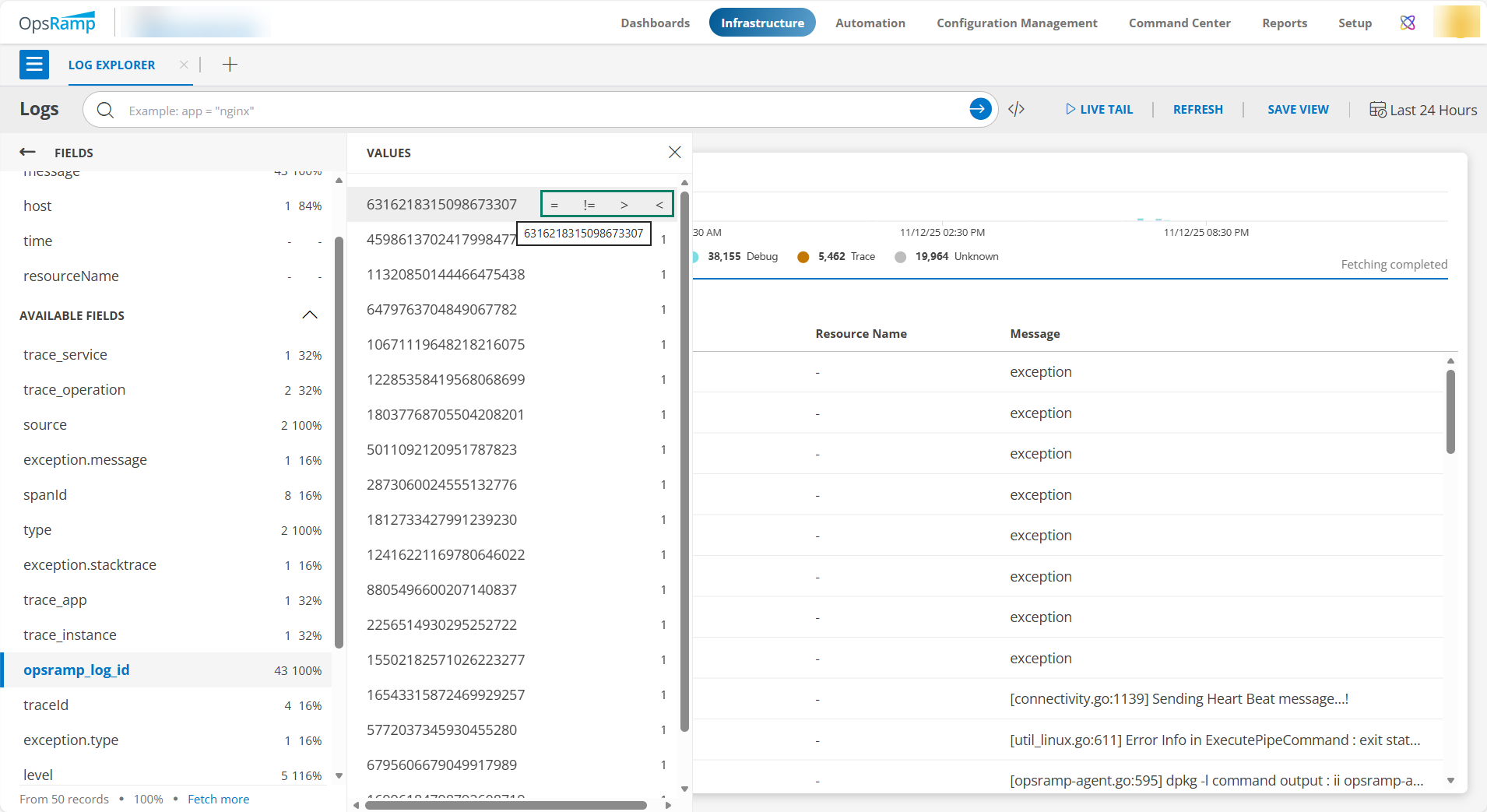
The following are details of various operators and query functions.
Basic Syntax
The standard format for label search queries follows:
Supported Operators
Equals (=)
Example: source = "agent"
Matches logs where the source is exactly "agent".
Not Equals (!=)
Example: source != "agent"
Matches logs where the source is not "agent".
Regex Match (=~)
Example: source =~ "agent"
Matches logs where the source matches the regex pattern "agent".

Not Regex Match (!~)
Example: source !~ "agent"
Matches logs where the source does not match the regex pattern "agent".

Combining Multiple Filters
Logical operators allow users to create more refined queries:
AND (| or AND)
Example: source = “agent” | level != "debug"
OR
source = “agent” AND level = "error"
Matches logs where both conditions are true.

OR (OR)
Example: source = “agent” OR source = "kubernetes"
Returns logs where the source is either “agent” or "kubernetes".

Grouping with Parentheses
Example: source = "agent" AND (level = "error" OR level = "warn")
Returns logs where the source is "agent" and the level is either "error" or "warn".

Using the IN and NOT IN Operators
These operators allow checking against multiple values, supporting both plain strings and regex patterns:
Match Exact Values
Example: source IN ("aws", "azure", "agent")
Matches logs where the source is "aws", "azure", or "agent".

Exclude Specific Values
Example: source NOT IN ("aws", "azure", "agent")
Excludes logs where the source is "aws", "azure", or "agent".

Regex Patterns
Example: source IN ("a.*")
Matches any source starting with "a " (e.g., "aws", "agent").
Exclude Using Regex
Example: source NOT IN ("a.*", "syslog")
Excludes logs where the source starts with "a " or is exactly "syslog ".
Note
- Values inside IN and NOT IN can be either plain strings or regular expressions.
- The IN operator is supported in Log Explorer, Alerts page, Metric page, and the Sear Logs API.
Using groupBy in the Advanced Query Builder
The groupBy function enables users to group logs by one or more fields, primarily for count-based aggregations. It is only supported in:
Log Tile (on the dashboard)
Log Metrics
If used elsewhere, the function will be ignored.
Example Usage
groupBy(source, level)
- Groups logs by source and level, counting entries for each unique combination.
More Query Examples
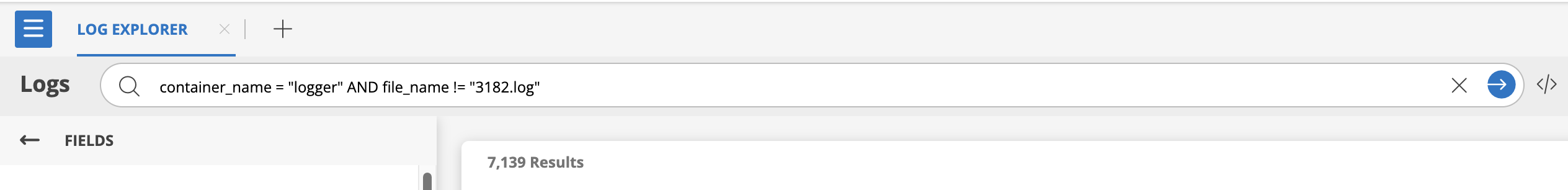
container_name IN ("logs-* ", "traces-*") AND container_name != "logs-query" AND level IN ("error" "fatal")
- Matches logs where:
- container_name matches "logs-" or "traces-".
- container_name is not "logs-query".
- level is "error" or "fatal".
source = "kubernetes" AND level != "debug"
- Matches logs from Kubernetes where the level is not "debug".
source IN ("agent", "syslog") AND message =~ "timeout"
- Matches logs where the source is either "agent" or "syslog", and the message contains "timeout" (regex).
env = "prod" AND (level = "error" OR level = "warn")
- Returns production logs where the level is either "error" or "warn".
container_name =~ "api-.*" AND level IN ("info", "error") AND message !~ "health"
- Matches logs where:
- container_name starts with "api-".
- level is "info" or "error".
- message does not contain "health".
service != "auth-service" OR status_code = "500"
- Matches logs where:
- The service is not "auth-service", or
- The status_code is "500".
Additional Functionalities
The additional functions for Advanced Query Builder include the following three functions.
- splitString – Splits a string into multiple parts based on a delimiter.
- SplitRegex – Uses regular expressions to split strings dynamically.
- parseJson – Extracts structured data from JSON strings for better analysis.
splitString Function
The splitString function is used to divide a string field into multiple parts based on a specified delimiter (e.g., :, -, _). It then extracts a specific part using a 0-based index. This is particularly useful when dealing with composite fields like container image names (gcr.io/my-image:latest) or log strings that follow a predictable format.
Syntax
splitString(field=<field_name>, by='<delimiter>', index=<number>) [AS alias_name]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| field | The field that contains the string you want to split. | Required |
| by | The delimiter used to split the string. | Required |
| index | Position to extract. | Required |
| AS alias_name | Optional alias for the result of the function. | Optional |
Default Behaviors
- If alias is not specified, the default alias is <field_name>[<index>].
Examples
Extract the second part with a custom alias
splitString(field=kubernetes_container_image, by=':', index=1) AS image_tag

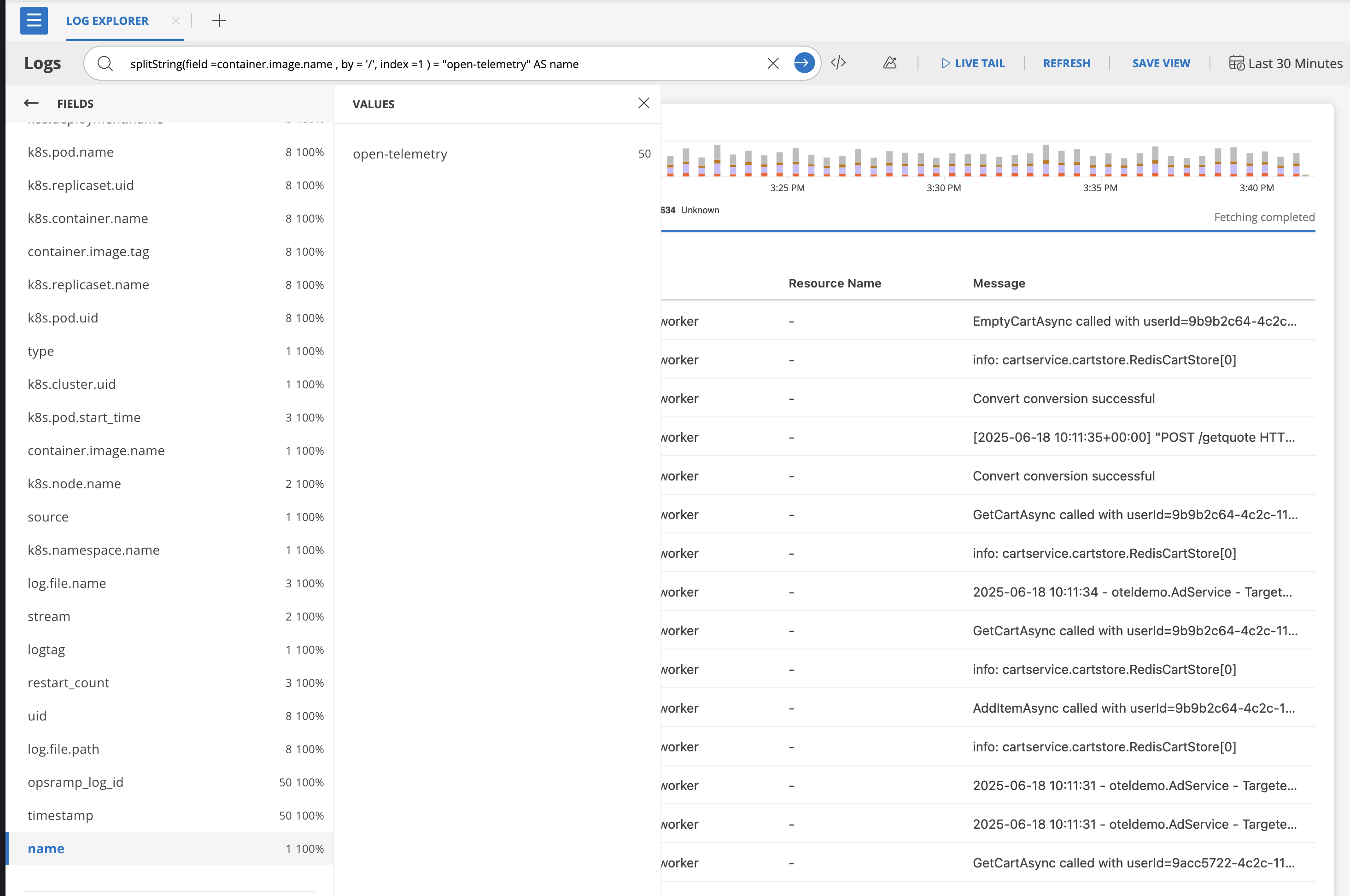
Compare extracted value to a specific value
splitString(field =container.image.name , by = '/', index =1 ) = "open-telemetry" AS nameMeaning: only match logs where name is exactly “open-telemetry”.
SplitRegex Function
The splitRegex function works like splitString, but uses a regular expression pattern for splitting. This is ideal when the delimiter is not fixed or is more complex.
Syntax
splitRegex(field=<field_name>, by='<delimiter>', index=<number>) [AS alias_name]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| field | The field to split. | Required |
| regex | Regular expression pattern to split on. | Required |
| index | Position to extract | Required |
| AS alias_name | Optional alias for the result of the function. | Optional |
Default Behaviors
- If alias is not provided, the default alias is <field_name>[<index>].
Examples
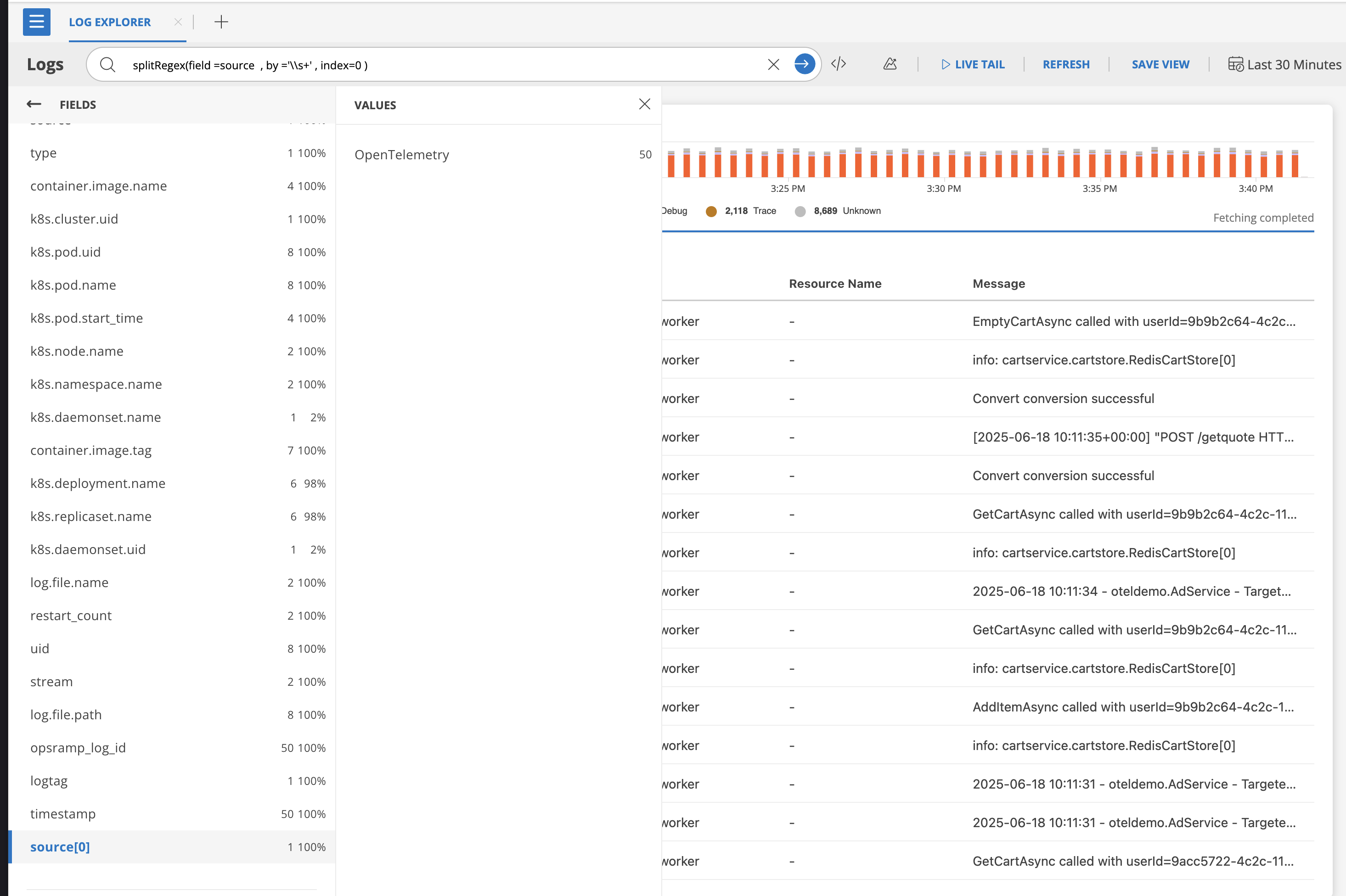
- Custom index with default alias
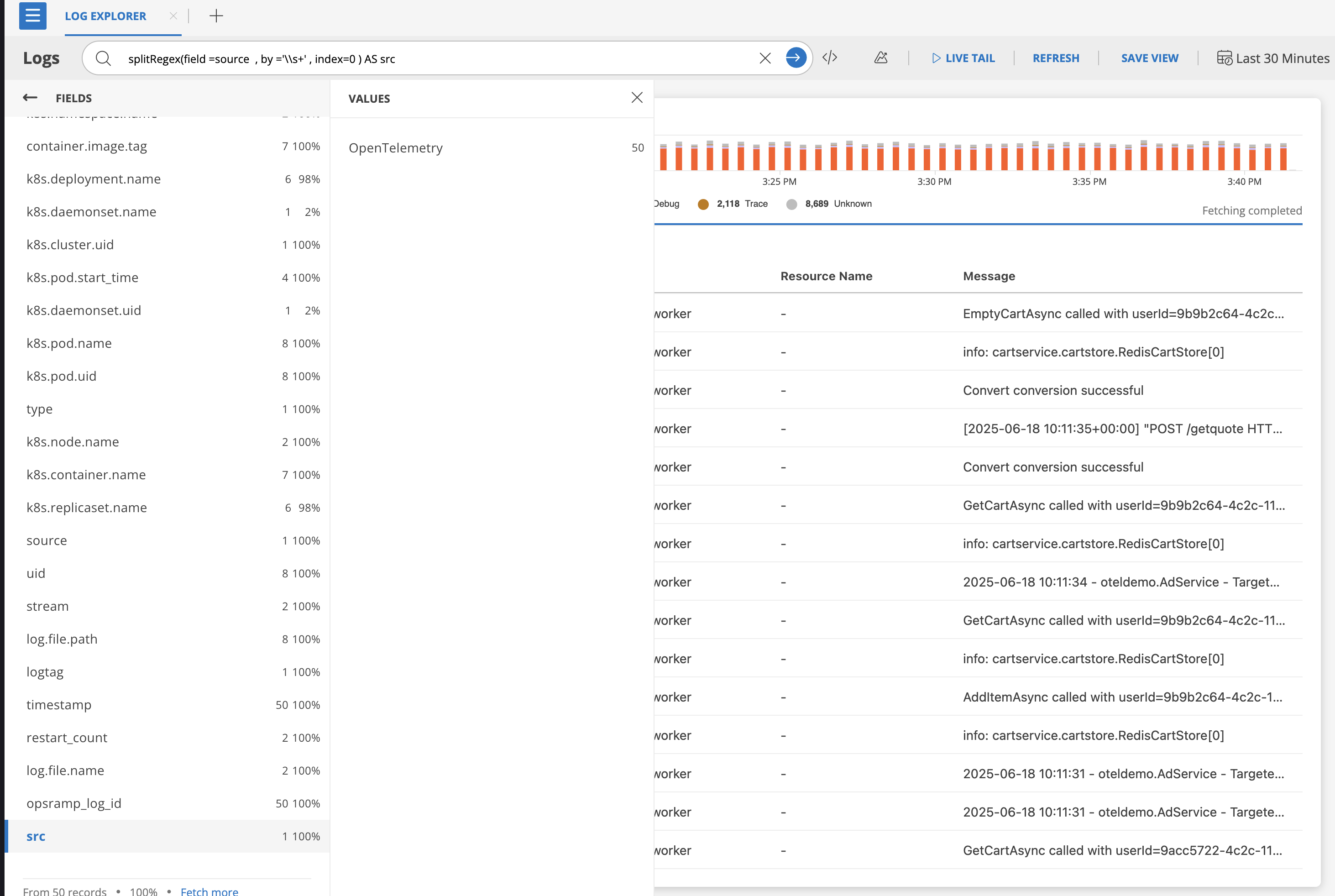
splitRegex(field=log, by='\\s+', index=8)
Creates alias: source[0]
- Custom index with custom alias
splitRegex(field=source, by='\\s+', index=0) AS src
parseJson Function
The parseJson function is designed to extract values from fields containing JSON-formatted strings. It uses dot notation to navigate nested JSON structures.
Syntax
parseJson(field=<field_name>, key=<json_path>) [AS alias_name]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| field | Field containing the JSON string. | Required |
| key | Dot-separated path to the desired key. | Required |
| AS alias_name | Optional alias name for the extracted value. | Optional |
Default Behaviors
- If no alias is specified, the alias defaults to the JSON key path (e.g. kubernetes.container_name).
Behavior Notes
- If the key path is not available, the result is null.
- Supports nested keys using dot notation.
Examples
- Extract a container name from nested JSON
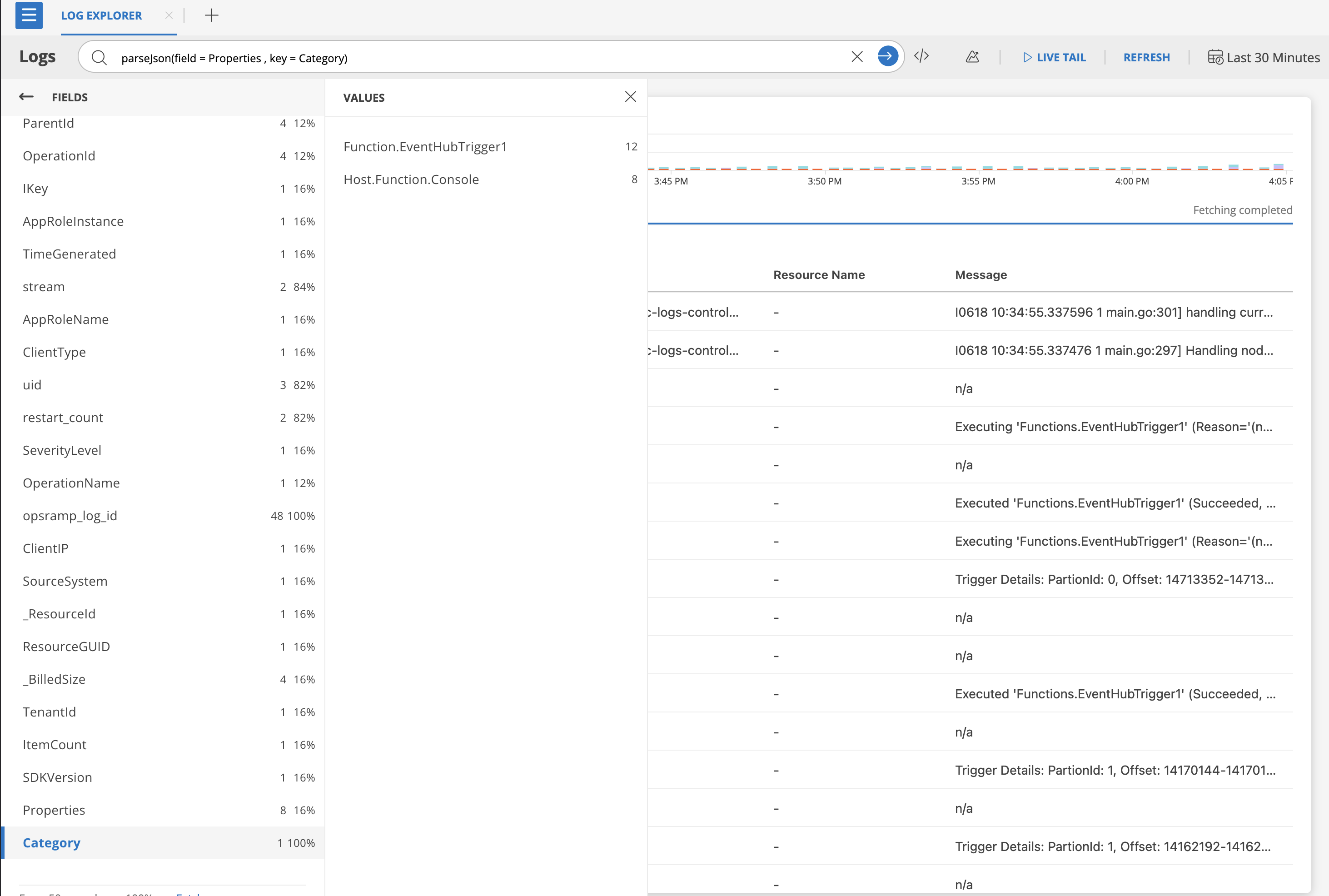
parseJson(field = Properties , key = Category)
alias: Category
- Use custom alias
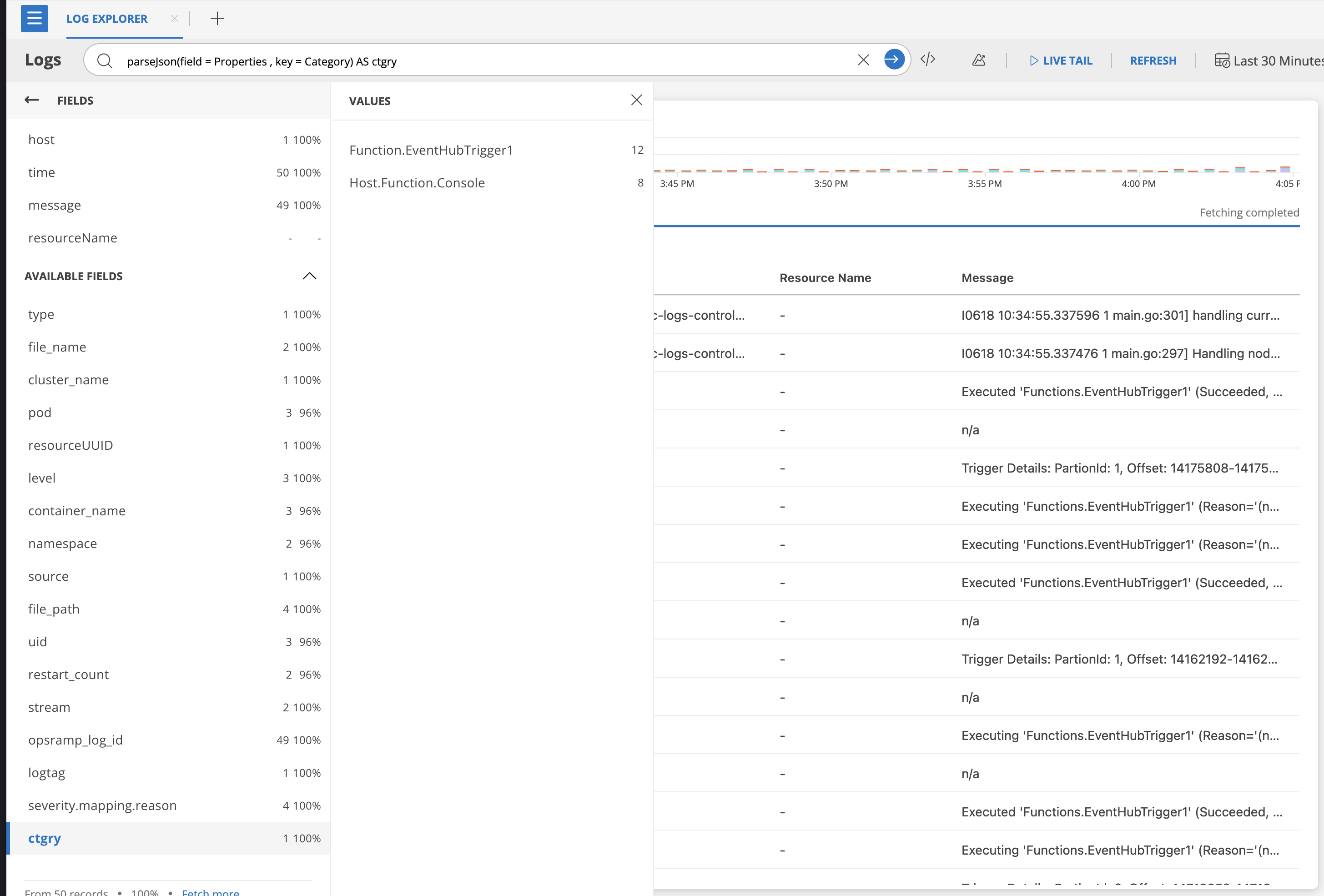
parseJson(field = Properties , key = Category) AS ctgry
alias: ctgry
Regex Extract Function
The regexExtract function extracts part of strings using regular expressions with named capture groups. Use this function to parse timestamps, extract log levels, identifiers, or capture custom patterns from unstructured strings.
Syntax
regexExtract(field=<field_name>, regex='<pattern>', group=<group_name>)
Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| field | The field contains the text to apply regex on. | Required |
| regex | A regular expression pattern to match. | Required |
| group | Named group to extract (if not specified, all groups are extracted) | Optional |
Default Alias Behaviors
- When you use named groups, the function outputs a separate field for each group, using the group name as the field name.
- If unnamed groups are used, the alias is <field_name>[<group_memebr>].
Behavior Notes
If the group is not found or doesn’t match, the result is null.
When no group is specified, all named groups are returned as separate fields.
When no group is specified, matching does not works.
Examples
- Extract year and month from date string
regexExtract(field=log, regex='(?<year>\d{4})-(?<month>\d{2})')
Extracted fields: year, month

- Extract named group
regexExtract(field=log, regex='(?<year>\d{4})-(?<month>\d{2})', group=year)
Extracts year

- Match named group
regexExtract(field=log, regex='(?<year>\d{4})-(?<month>\d{2})', group=year) = '2025'

Comparision operators
| Application Name | Description | Version |
|---|---|---|
| > | Greater than | splitString(...) > 1.2 |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | parseJson(...) >= 100 |
| < | Less than | splitRegex(...) < 0 |
| <= | Less than or equal to | splitString(...) <= 5.0 |
| BETWEEN ... AND | Inclusive range comparison | label BETWEEN 1 AND 20 |
| NOT BETWEEN ... AND | Outside of an inclusive range | ... NOT BETWEEN 2020 AND 2023 |
You can combine comparison operators with transformation functions like splitString, splitRegex, parseJson, and regexExtract.
splitString
-- Extract and compare container image tag
splitString(field=kubernetes_container_image, by=':', index=2) = 19.2 AS image_tag
-- Filter image tags greater than 19.2
splitString(field=kubernetes_container_image, by=':', index=2) > 19.2 AS image_tag
splitRegex
-- Filter region values greater than 'us-east'
splitRegex(field=env_field, regex=':', index=2) > 2 AS region
parseJson
-- Compare extracted CPU usage
parseJson(field=log, key=metrics.cpu) BETWEEN 0.2 AND 0.8 AS cpu_bucket
regexExtract
-- Compare extracted year
regexExtract(field=log, regex='(?<year>\d{4})', group=year) >= 2022 AS extracted_year
Using Comparison Operators with Labels
--Extracts year BETWEEN 2021 AND 2025
year BETWEEN 2024 AND 2025